Deploying Flows Programmatically
Besides running flows via an API, you can deploy flows to one of the production orchestrators supported by Metaflow programmatically. For instance, you can use this feature to create a deployment script running as a part of your CI/CD system, e.g. on GitHub Actions, to deploy a flow to production automatically after a pull request has been approved.
For a practical example of Deployer in action, see
the sweep example in Config-Driven
Experimentation.
Deploying to production with the Deployer API
Deployments are handled through the Deployer API which follows closely the
command line interface used to push flows to production orchestrators like
Argo Workflows and
Step Functions.
This diagram outlines the deployment process and the objects involved:
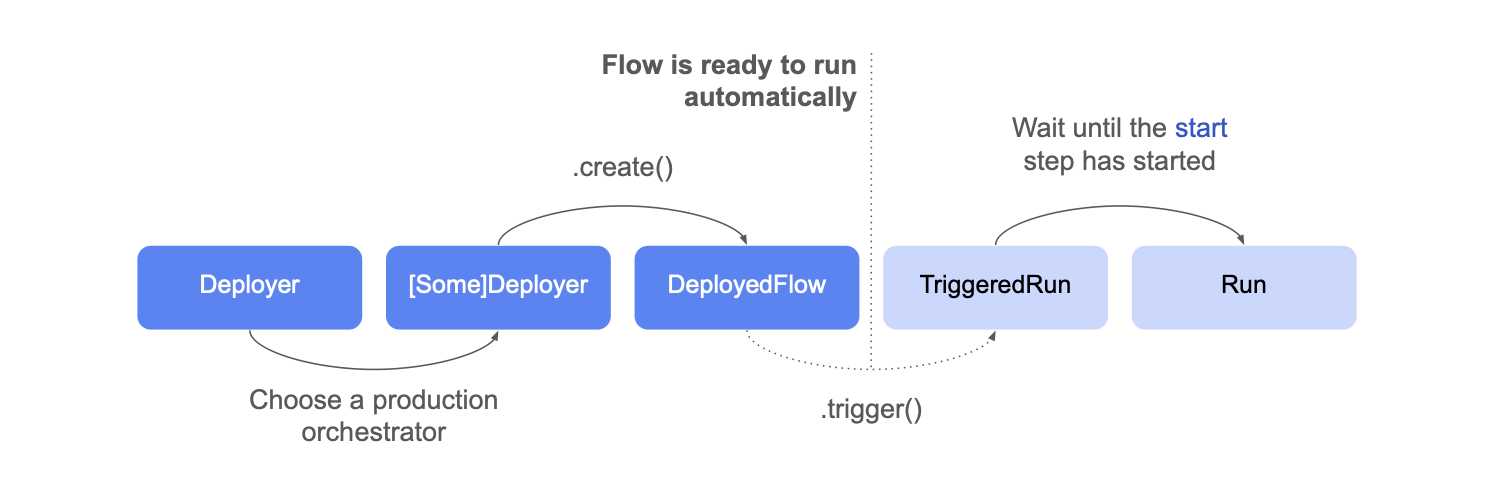
- Instantiate a
Deployerclass pointing at the flow file you want to deploy:
from metaflow import Deployer
deployer = Deployer('helloflow.py')
- Choose an orchestrator - here Argo Workflows - and call
create()to deploy the flow
deployed_flow = deployer.argo_workflows().create()
The flow is now scheduled for execution! If you had annotated the flow
with a @schedule decorator, it would
run automatically at the desired time.
Had you annotated it with @trigger,
or @trigger_on_finish, it would
run automatically when the specified event arrives.
Triggering a flow explicitly
You can trigger a deployed flow explicitly by calling trigger()
triggered_run = deployed_flow.trigger()
You can specify any Parameters
in trigger, e.g.
triggered_run = deployed_flow.trigger(alpha=5, algorithm='cubic')
Triggering returns a TriggeredRun object, representing a run that is
about to get scheduled by the orchestrator. Only when the start
step starts executing, a corresponding Run object
becomes accessible. This may take a while, for instance, if a new
cloud instance needs to start to execute the task:
# wait for the run object to be available, timeout None means wait forever
run_obj = triggered_run.wait_for_run(timeout=None)
print('Run started', run_obj)
Terminating a triggered run
You may terminate a triggered run at any time by calling
triggered_run.terminate()
Accessing Previously Deployed Flows
You can retrieve an existing deployed_flow object using the
from_deployment method instead of creating a new deployment. This allows
you to work with flows that were previously deployed without having to call
create() again.
Once you have the deployed_flow object, you can use its trigger() method to
create a triggered_run object and execute the flow. This approach is
particularly useful when you need to reference and run existing deployments
rather than creating fresh ones.
from metaflow import Deployer
deployer = Deployer('helloflow.py')
deployed_flow = deployer.argo_workflows().create()
# save this for later use...
identifier = deployed_flow.name
from metaflow import DeployedFlow
# use the identifier saved above..
deployed_flow = DeployedFlow.from_deployment(identifier=identifier)
triggered_run = deployed_flow.trigger()
The from_deployment method is only available for argo-workflows at the moment.
Orchestrator-specific methods
Besides the common methods highlighted above, each orchestrator exposes
additional methods for managing deployments and triggered runs. For details,
see the API documentation for Deployer.
Currently, Deployer doesn't support deployments to Apache Airflow, as Airflow
doesn't expose an API for deployments. Instead, you should
copy the resulting Airflow dag
manually to your Airflow server.